Drink Motivation Quiz (DMQ)
Reframing a Chatbot-only behavioural tool into a journey-led experience aligned with user readiness and strategy.
Organisation: Drinkaware
Role: UX Designer
Overview
The Drink Motivation Quiz (DMQ) is an existing behavioural tool that was originally launched within Drinkaware’s Chatbot in 2022. While it engaged users, its reach was limited, and results lacked actionable insight.
I was tasked with exploring how to evolve the DMQ into a broader, strategic tool that engages users with low risk-recognition, captures meaningful motivation data, and supports onward journeys toward behaviour change.
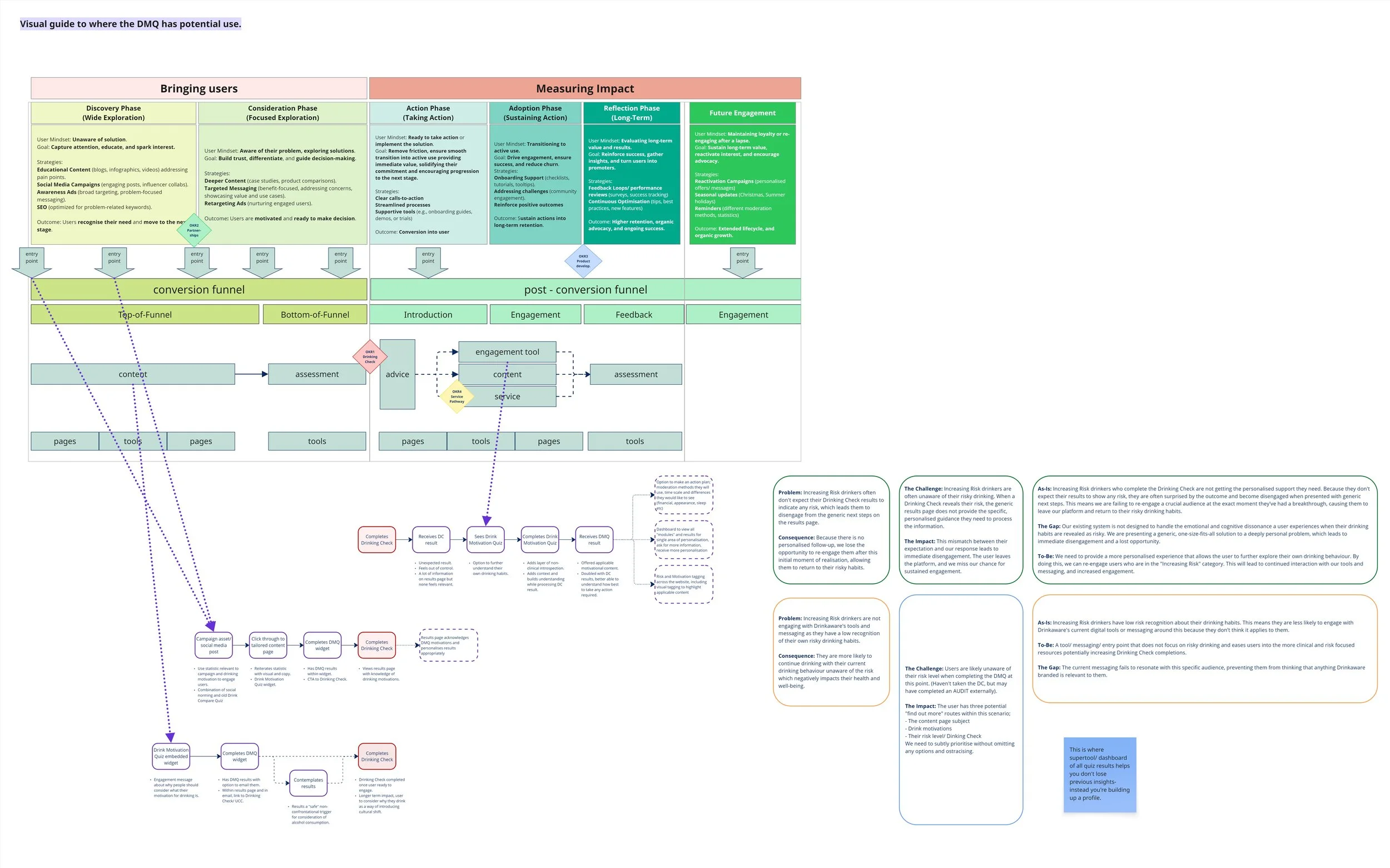
Reframing the Challenge
I began by focusing on how DMQ results were visualised, but designing in isolation didn’t address the bigger picture. Without understanding where users were coming from, the organisation’s goals, or how success would be measured, the approach lacked strategic focus.
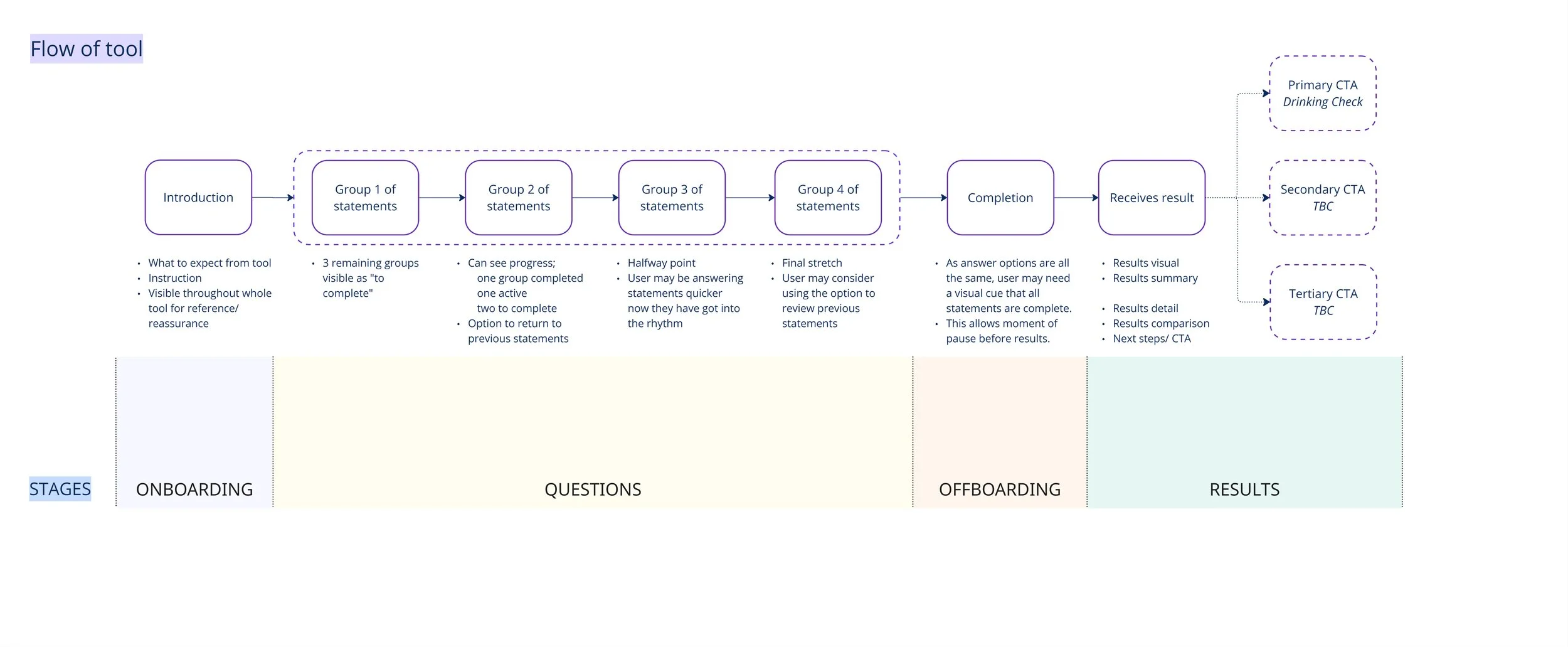
To address this, I mapped a user flow breaking the tool into three stages:
Onboarding and Offboarding
The Questionnaire
Results and Onward Pathways
Reviewing research, testing insights, service blueprint data, and the current tool highlighted user needs and opportunities at each stage. These insights directly informed the design recommendations, giving each solution a clear rationale and measurable intent.
Applying the new 2026-2031 Strategy: During this project, the release of the 2026–31 strategy prompted me to pause and review my work to date. I ensured the DMQ’s aims aligned with the wider organisational goals, considered its placement within the digital funnel, and refined the target audience to maximise relevance and engagement.
Discovery and User Insight
Key limitations of the current tool:
The current DMQ results are highly binary- users either have or do not have a motivation- which conflicts with the scaled nature of the questions. This makes it difficult for users to:
Understand which motivations matter most
Take meaningful action
Compare outcomes or track change over time
User feedback highlighted:
Desire for context and transparency around scores
Interest in how results were calculated and how to move to a lower risk level
Motivation tools need explanation and actionable next steps to feel credible
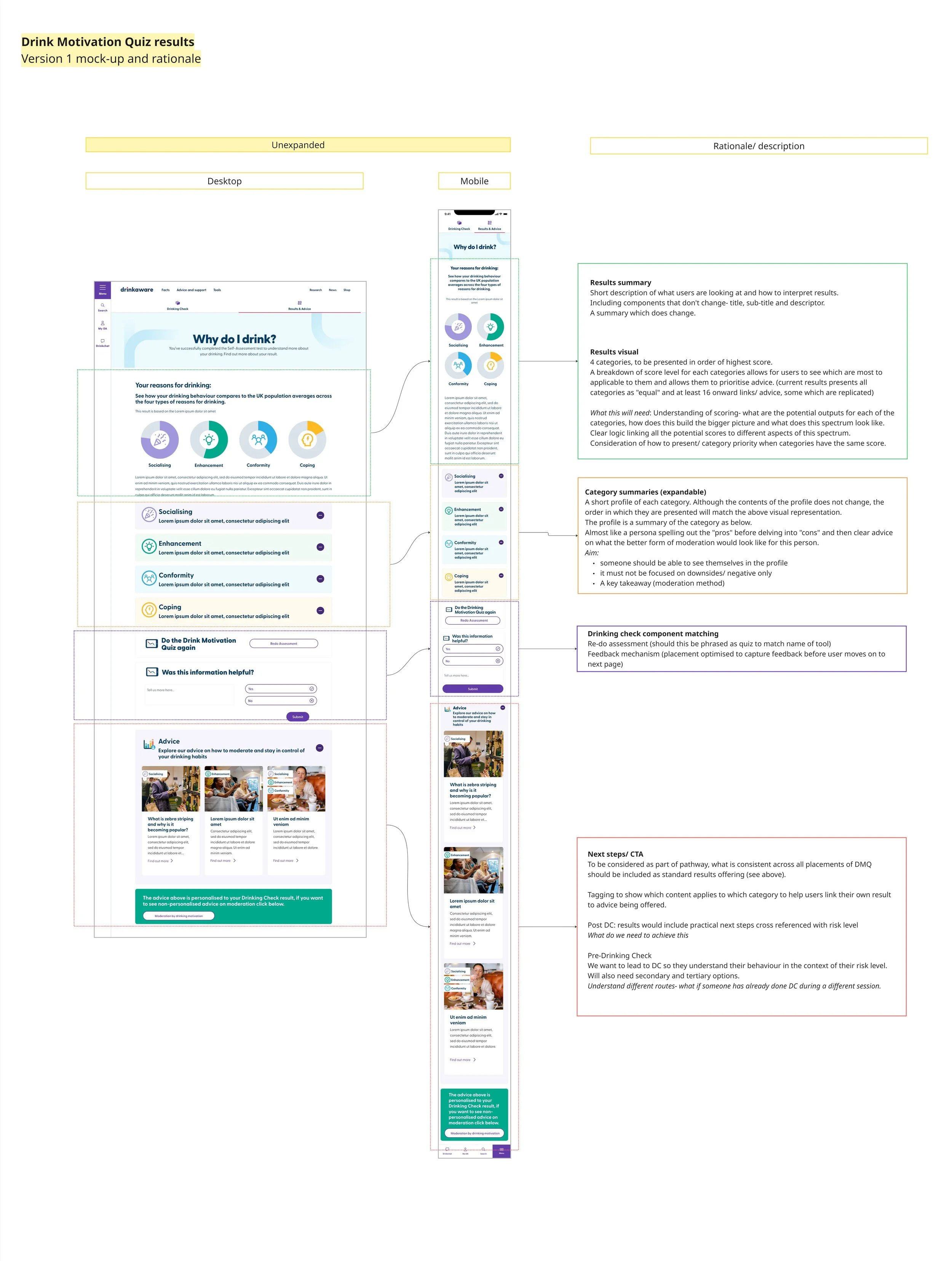
Initial results page mockup
DMQ User flow
Wireframe showing the grouping of questions
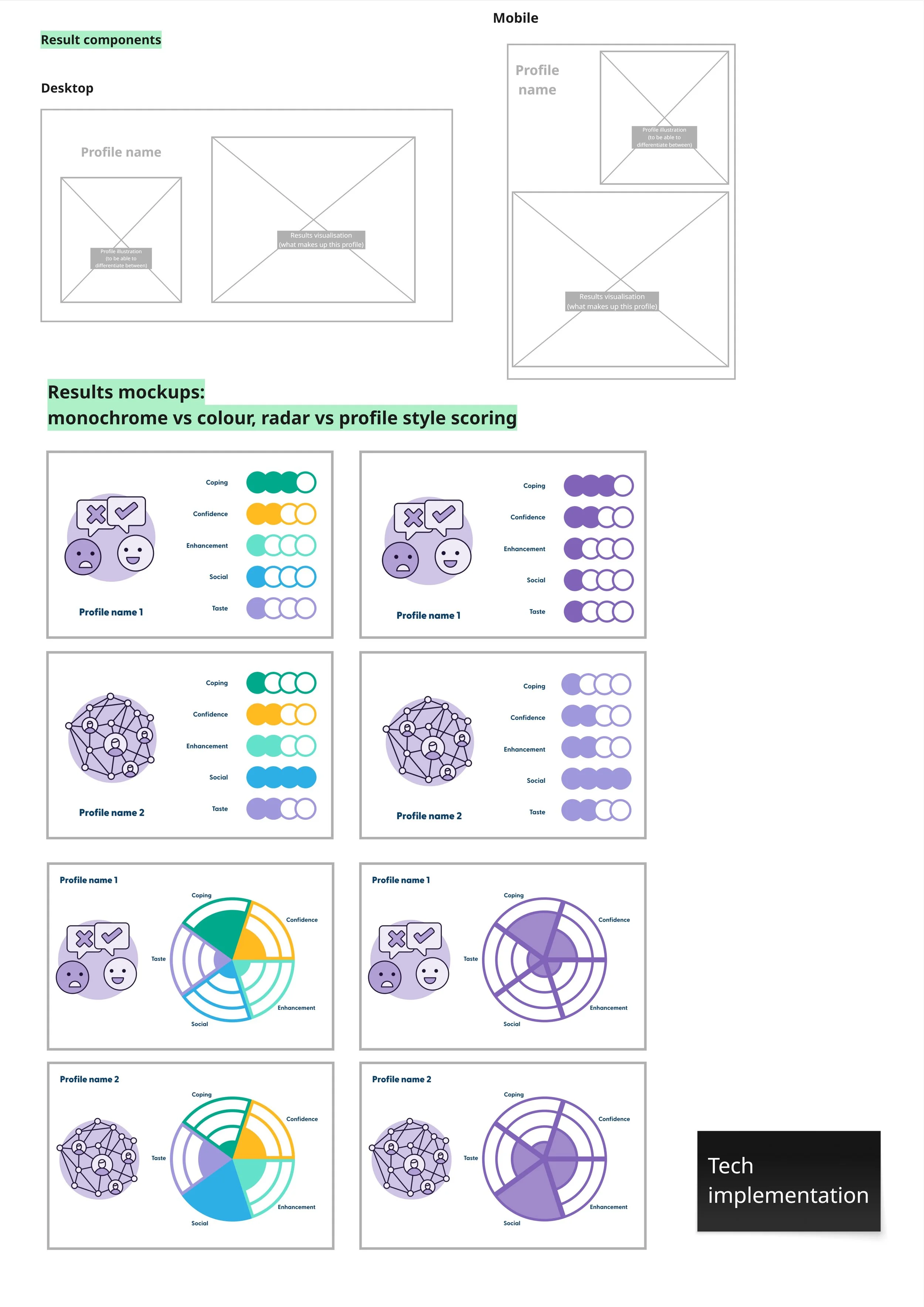
Results mock-ups
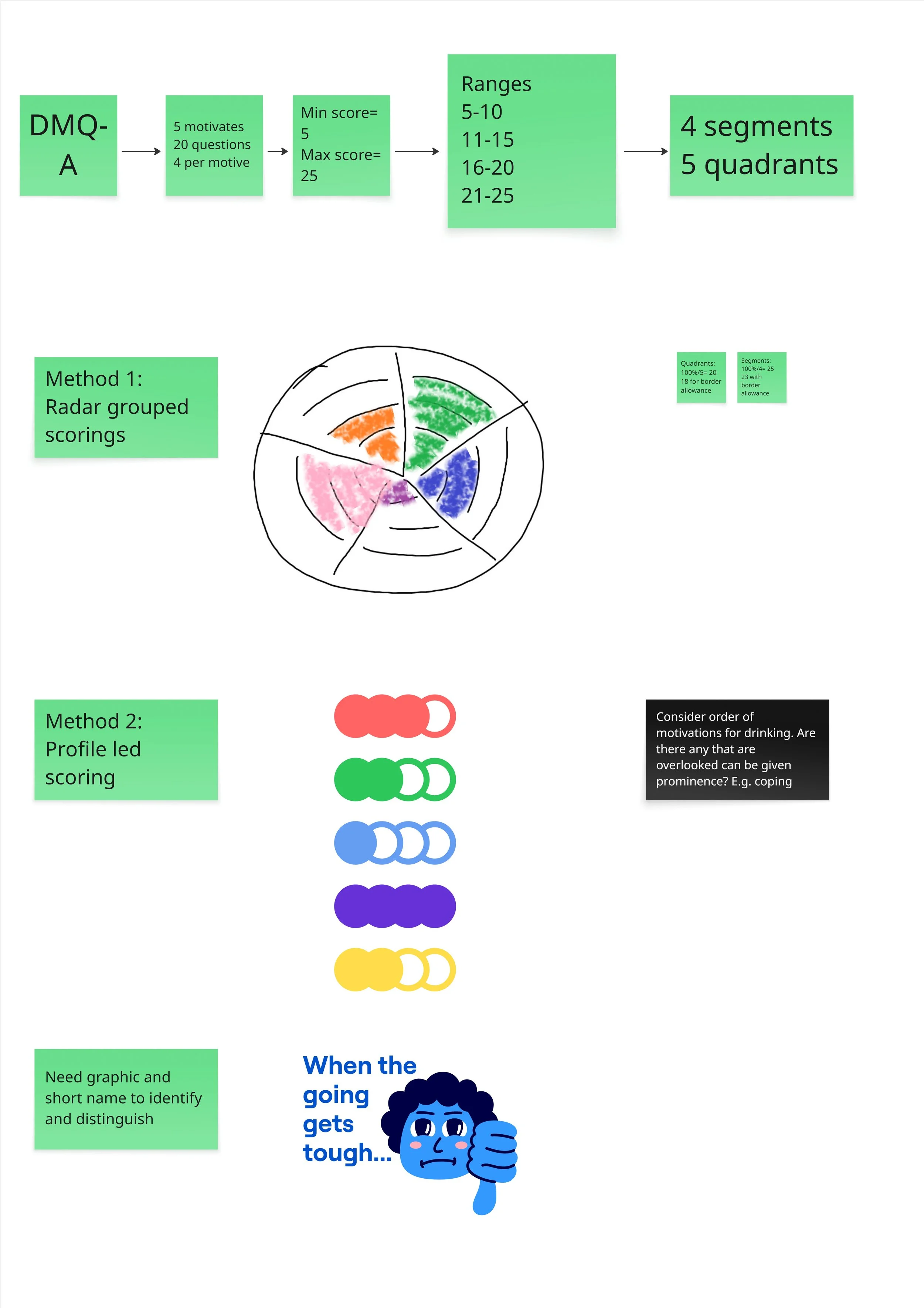
Lo-fi results visual planning
Mapping of potential DMQ use cases
Solution Development
Based on the insights gathered across the journey, I developed a set of design recommendations to address user needs at each stage of the tool.
Questionnaire
I recommended the following changes to better reflect the target audience and support accurate scoring:
A switch to DMQ-A, an adult-focused version with updated motivations (removed Conformity, added Confidence and Taste) that better reflect our audience.
Maintain first-person framing: “I drink because…”
Group 20 questions into four sets of five to reduce fatigue and create a sense of progress
Enable back navigation and remove the skip option to maintain scoring integrity and personalisation
The Importance of Onboarding and Offboarding:
I recommended treating onboarding and offboarding as critical moments in the journey- at the top of the funnel, users can disengage easily. Onboarding and offboarding provide context, set expectations, and guide reflection, helping users understand why they’re there and keeping them engaged throughout the experience.
Results
I recommended that results function as a gateway rather than an endpoint, guided by the following principles:
Keep results simple, visual, and actionable
Enable continuity if users stop and return (something not offered across our other tools)
To support this, I recommended profile-based results, grouping motivation scores into clear ranges (5–10, 11–15, 16–20, 21–25). This approach summarises multiple inputs into a single, meaningful outcome, reducing cognitive load and making results easier to understand and act on.
Each profile would use a short name and supporting graphic, helping users quickly recognise their result and focus on what it means and where to go next, rather than on individual scores.
Success Metrics
To evaluate the DMQ once live, I recommended tracking success across two key areas, directly informed by the user flow:
1. User Journeys- How effectively users enter and move through the tool:
Click-throughs from placement or campaigns
Progression to the Drinking Check and other CTAs
Reaching intended next steps within a defined number of pages
2. Engagement with the Tool- How users interact within the DMQ:
Start rate (low landing-page drop-off)
Completion rate (high overall completion)
These recommendations ensure that both funnel progression and engagement are captured, providing a clear framework for evaluating the tool’s impact once implemented.
Next Steps
After presenting draft recommendations to stakeholders within the Directorate, feedback was incorporated and the recommendations were formalised in a report to guide the next stage of the project in 2026. Key planned activities include:
Design end-to-end user journeys- Map realistic pathways for the primary audience using existing webpages and personas. This will illustrate example routes into the DMQ and show how users can be guided to the Drinking Check via secondary routes within a set number of pages if they don’t engage with it immediately.
Wireframe results pages- Visualising how users will see and interact with their outcomes
Develop and refine scoring models- Ensuring accurate and meaningful motivation-based profiles
Design results profiles- Simplifying complex data into actionable insights
Plan and conduct user testing- Validate assumptions and optimise the experience before handing over to an external agency for build
Reflection
This project reinforced the value of stepping back to understand the full user journey and aligning design with organisational goals. Mapping the DMQ flow and identifying user needs at each stage strengthened my skills in problem framing and translating insights into actionable recommendations, showing how thoughtful design can drive engagement and measurable outcomes.
This approach lays a strong foundation for prototyping, testing, and implementing a journey-led DMQ in 2026.